[Completed] “Advanced communication and control for the prevention of blackouts”, DST-UKIERI research collaboration, 2014-18 (Co-PI)
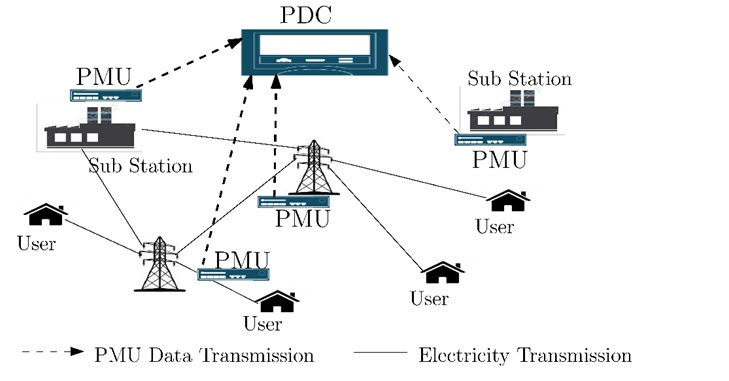
Figure: Wide-area measurement system
On the smart grid health monitoring, considering the time-critical nature of data and large-scale grid stability issues involved, a novel data driven framework is proposed based on ϵ-Support Vector Regression to reduce the bandwidth requirement for transmission of Phasor Measurement Unit (PMU) data. This is achieved by judicious elimination of redundant data at the PMU before transmission. Simultaneously, the missing samples are predicted at Phasor Data Concentrator (PDC) to ensure faithful identification of impending disturbances in the power system. Compared to the competitive data reduction scheme, the proposed algorithm saves around 60% bandwidth and identifies power system disturbances 73% more accurately. Similar to the PMU data, telemetric data such as in smart metering is another source of data which is expected to increase the volume of network traffic simultaneously, though it does not possess the same nature of dynamics. A novel characterization of such data based on Gaussian mixture model is presented. Further, at each end node, sparsity of data is exploited to devise an adaptive data reduction algorithm using compressive sampling technique such that the bandwidth requirement for field data transmission is reduced with minimum loss of information. Specifically, an adaptive data reduction scheme using compressive sampling is devised to operate at the smart meter which achieves about 40% bandwidth saving in data transmission to the nearest collection center.
(Reference: IEEE Trans. Ind. Informat., 2018a; IEEE Trans. Ind. Informat., 2018b)
[Students: Sharda Tripathi, Mayukh Roy Chowdhury]
