[Completed] "Unified cross-layer approach to energy saving measures in wireless sensor networks", CSIR, 2007-10 (PI)
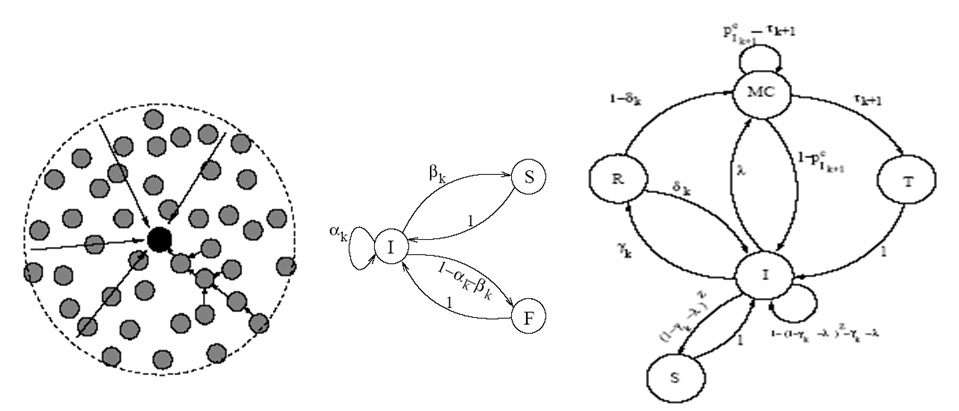
(a) (b) (c)
Figure: (a) Many-to-one transmission model, (b) channel model, (c) node model
In wireless ad hoc and sensor networks, irrespective of whether the communications are one-to-one (ad hoc communication between two mobile computers) or many-to-one (field nodes to the data sink), energy consumption and the network lifetime maximization issue is a critical issue. To this end, in this project we have focused on energy consumption characterization in many-to-one and one-to-one multihop data forwarding, where we have implicitly assumed the data are delay tolerant. We have then addressed the issue of network lifetime maximization via new protocol level solutions, such as optimum forwarding node selection, optimum forwarding strategies, and transmit power control. We have also obtained some proof of concept results on network RF (radio frequency) energy scavenging to increase the network lifetime or in some case for perpetual network operation of rudimentary field sensor nodes from the available network RF energy. We have addressed four distinct, yet mutually complementing aspects:
- channel-aware link layer retransmission strategies,
- radio receiver properties aware optimum MAC layer carrier sensing,
- channel and link aware network layer optimum forwarding strategies, and
- channel aware transmit power control implementation strategies.
[Students: Bighnaraj Panigrahi, Priyatosh Mandal]
